11 min read
Overview
Want to build an add-on but not sure how to manage user access? Quicknode supports four authentication methods, each designed for different use cases and security requirements. Whether you're building an open public service, need simple access control, or require complex user management, there's an authentication option that fits your needs.
This guide explores the different authentication methods available for Quicknode Marketplace add-ons, Header-Based Authentication, HTTP Basic Auth, traditional Provisioning APIs, and No Authentication. This guide explores each method, helping you choose the best approach for your service based on your specific requirements.
What You Will Learn
- The different authentication methods available for Quicknode Marketplace add-ons
- The benefits and trade-offs of each method
- Implementation examples for each authentication method
What You Will Need
- A Quicknode partner account
- Familiarity with HTTP requests and responses
- Basic understanding of API concepts and Web3 development
If you don't have a Quicknode partner account yet, it's easy to get started. After logging in to your Quicknode dashboard, click on the avatar icon on the top left and select the Switch to Partners tab, and then complete the marketplace account application. Approval process for new Marketplace partners may take up to 7 business days, however, you can generally expect a response in 1-2 business days.
Authentication Methods
The Quicknode Marketplace supports multiple authentication methods to integrate your API, making it easier than ever to onboard without requiring code changes on your end.
Before diving into the details of each method, here's a quick overview of all the authentication options available for Quicknode marketplace add-ons:
| Method | Best when… | Key benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Header‑Based Auth (any HTTP header) | Your API already expects a header. | Zero code changes. Quicknode forwards the header exactly as provided. |
| HTTPS Basic Auth | You need a single username/password pair for all Marketplace traffic. | Simple to set up and minor code changes. |
| Custom Provisioning API | You must implement custom endpoints for user lifecycle management and/or your add-on includes a dashboard or supports SSO login. | Full control over customer lifecycle. |
| No Auth | Your service is meant to be fully public (e.g. Flashbots Protect). | Frictionless for both partner and users. |
Note: Quicknode handles rate limiting for all authentication methods, so you don't need to implement your own rate limiting logic.
1. Header-Based Authentication
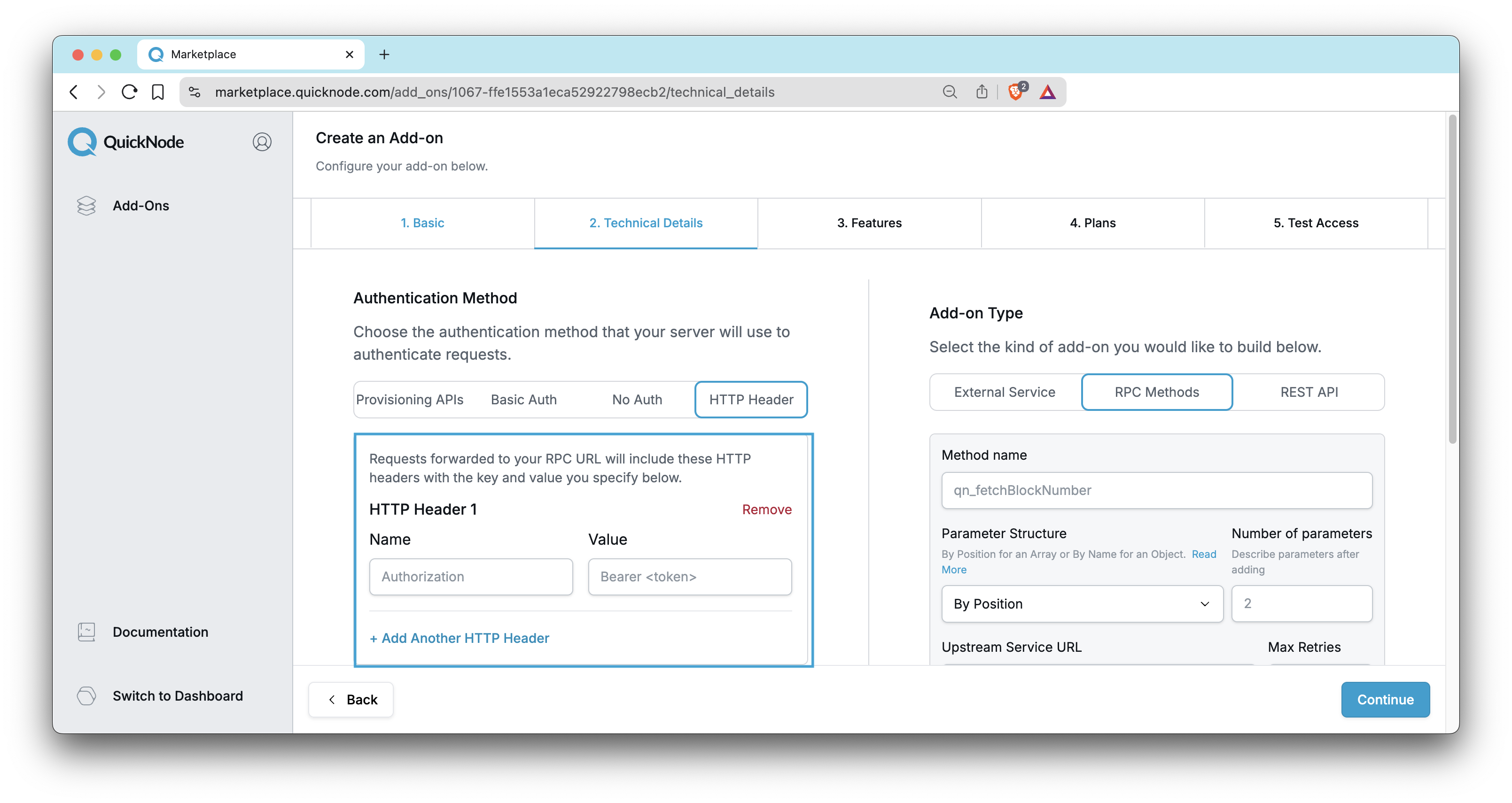
This method allows you to use any custom HTTP header for authentication. You can define the header name and the secret value that Quicknode will use to authenticate requests to your API. This option allows direct integration of your existing API without requiring any code changes on your end, provided your API already supports header-based authentication.
When Quicknode forwards requests to your API, we automatically include several identification headers alongside your custom authentication header:
X-QUICKNODE-ID: The customer's unique IDX-INSTANCE-ID: The specific endpoint ID for this requestX-QN-CHAIN: The blockchain networkX-QN-NETWORK: The network environmentX-QN-TESTING: Present during Quicknode QA testing (helps identify test traffic)
For Strict APIs: If your existing API validates incoming headers strictly and rejects requests with unexpected headers, you may need to configure it to accept these additional headers.
If you're interested in joining the Quicknode Marketplace with your API, it's as simple as providing the header name and value during the add-on setup process. Also, our Marketplace team can potentially build the integration for you.
Implementation Example
Here's a simple example of how to implement Header-Based Auth in your add-on service using Express.js:
import { Router } from 'express'
const router = Router()
// Middleware to validate custom header
const validateCustomHeader = (req, res, next) => {
const apiKey = req.headers['x-api-key'] // Your custom header name
const expectedKey = process.env.CUSTOM_API_KEY
if (!apiKey || apiKey !== expectedKey) {
return res.status(401).json({ error: 'Unauthorized: Invalid API key' })
}
next()
}
router.post('/rpc', validateCustomHeader, async (request, response) => {
// Extract Quicknode headers for enhanced functionality
const quicknodeId = request.headers['x-quicknode-id']
const instanceId = request.headers['x-instance-id']
const chain = request.headers['x-qn-chain']
const network = request.headers['x-qn-network']
const isTesting = request.headers['x-qn-testing'] === 'true'
// Process the authenticated request
const { method, params } = request.body
// Your service logic here
const result = processRequest(method, params, { quicknodeId, chain, network, isTesting })
response.json({
jsonrpc: '2.0',
result: result,
id: request.body.id
})
})
2. HTTP Basic Auth Protection
HTTP Basic Auth provides a lightweight and secure way to protect your Marketplace add-on endpoints without the need for custom provisioning APIs. When you select this option, Quicknode includes a standard HTTP Basic Auth header in every request forwarded to your add-on's service endpoint.
If you select HTTP Basic Auth protection, requests forwarded to your service endpoint will include a Basic Auth HTTP Header. This header is in the format Authorization: Basic <credentials>, where <credentials> is the Base64 encoding of a username and password joined by a single colon (e.g., username:password). Your add-on service is responsible for validating these credentials with each incoming request.
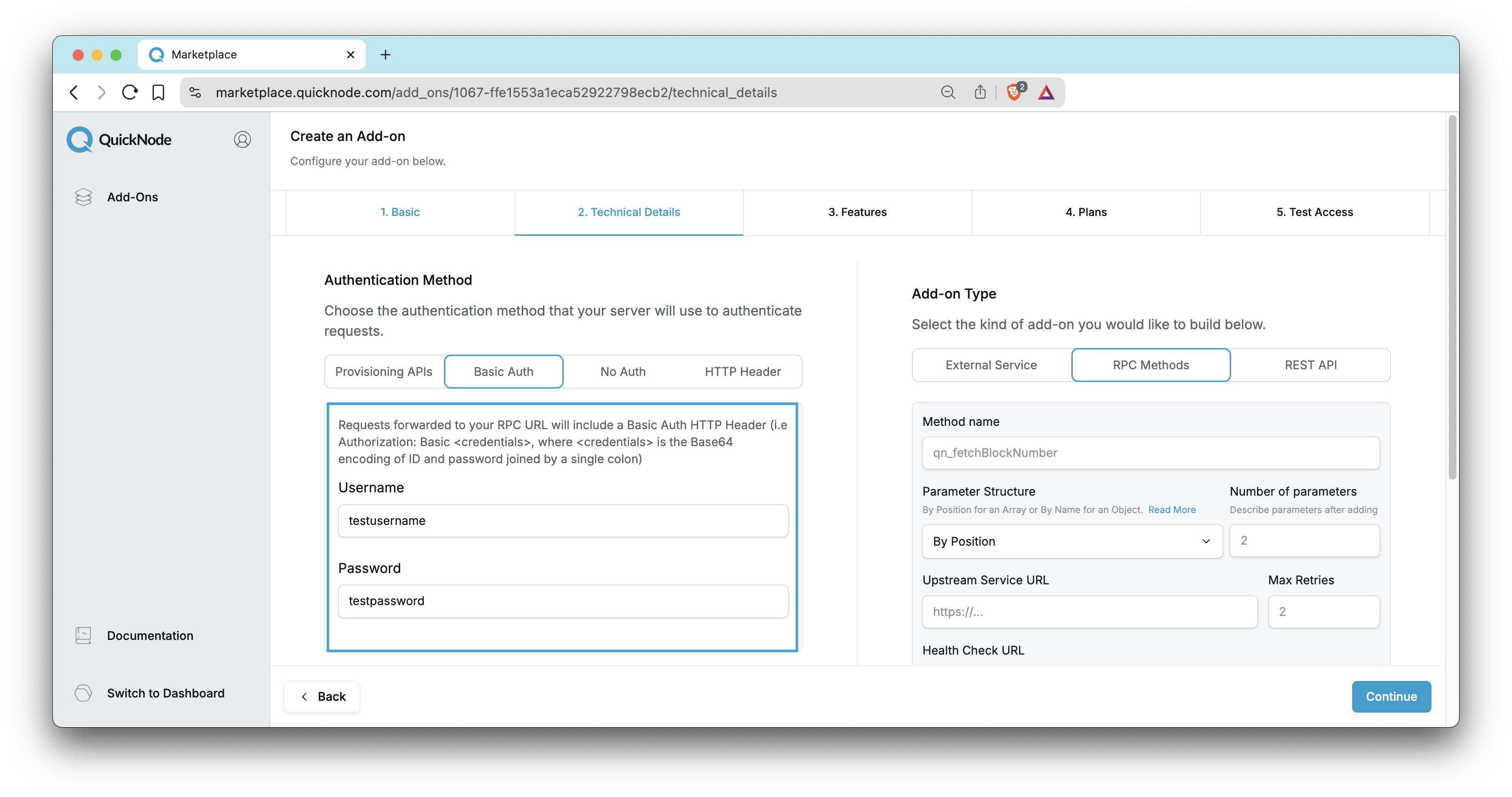
Quicknode securely stores the username and password you provide during the add-on setup and automatically generates the Base64 encoded string for inclusion in the Authorization header.
Example of an Authorization header, where Aladdin is the username and open sesame is the password:
Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ==
When Quicknode forwards requests to your API, we automatically include several identification headers in addition to the Authorization: Basic header:
X-QUICKNODE-ID: The customer's unique IDX-INSTANCE-ID: The specific endpoint ID for this requestX-QN-CHAIN: The blockchain networkX-QN-NETWORK: The network environmentX-QN-TESTING: Present during Quicknode QA testing (helps identify test traffic)
For Strict APIs: If your existing API validates incoming headers strictly and rejects requests with unexpected headers, you may need to configure it to accept these additional headers.
Implementation Example
Here's a simple example of how to implement HTTP Basic Auth in your add-on service using Express.js:
import { Router } from 'express'
const basicAuth = require('express-basic-auth')
const router = Router()
// Provisioning API is behind basic auth
const authDetails = {}
authDetails[process.env.BASIC_AUTH_USERNAME] = process.env.BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD
const authInfo = {
users: authDetails,
challenge: true,
unauthorizedResponse: 'Not Authorized',
}
// Apply the basicAuth middleware to your RPC endpoint.
// Any request to '/rpc' will first be authenticated using the provided credentials.
router.post('/rpc', basicAuth(authInfo), async (request, response) => {
// Extract Quicknode headers for enhanced functionality
const quicknodeId = request.headers['x-quicknode-id']
const instanceId = request.headers['x-instance-id']
const chain = request.headers['x-qn-chain']
const network = request.headers['x-qn-network']
const isTesting = request.headers['x-qn-testing'] === 'true'
// Process the authenticated request
const { method, params } = req.body
// Your service logic here - can use header info for routing/access control
const result = processRequest(method, params, { quicknodeId, chain, network, isTesting })
response.json({
jsonrpc: '2.0',
result: result,
id: request.body.id
})
})
3. Provisioning APIs
Traditional provisioning APIs provide maximum flexibility and control over user management, usage tracking, and access control. This method requires implementing custom endpoints for user lifecycle management. With this approach, Quicknode interacts with a set of APIs you provide to automate the lifecycle of user subscriptions.
If your add-on includes a dashboard or supports SSO login, you must implement the Provisioning API method. The dashboard-url or access-url are returned in the provisioning response.
Required Endpoints
You need to implement these key endpoints for provisioning APIs:
| Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|
/provision | Creates a new instance of your add-on after a user is successfully charged |
/update | Updates an existing add-on instance when a user makes changes |
/deactivate_endpoint | Deactivates a specific endpoint associated with your add-on |
/deprovision | Removes an add-on instance when a user unsubscribes |
Security
All provisioning endpoints must be protected with HTTP Basic Auth. Quicknode provides you with a unique username and password during Marketplace onboarding (visible in your add-on’s Security tab).
- These credentials are unique to your account and must not be shared.
- You must verify every request against these credentials. If you skip verification, you risk serving fraudulent traffic and not getting paid.
- Any request containing the
X-QN-TESTINGheader comes from Quicknode’s testing tools and should be handled appropriately.
Provisioning Flow
Provision
It is triggered after a user successfully pays for your add-on.
- Quicknode sends a POST
/provisionrequest with payload details likequicknode-id,endpoint-id,plan, URLs, and optionalreferers.
{
"quicknode-id": "9469f6bfc411b1c23f0f3677bcd22b890a4a755273dc2c0ad38559f7e1eb2700",
"endpoint-id": "2c03e048-5778-4944-b804-0de77df9363a",
"plan": "your-plan-slug",
"wss-url": "wss://long-late-firefly.quiknode.pro/2f568e4df78544629ce9af64bbe3cef9145895f5/",
"http-url": "https://long-late-firefly.quiknode.pro/2f568e4df78544629ce9af64bbe3cef9145895f5/",
"referers": ["quicknode.com"],
"contract-addresses": [],
"chain": "ethereum",
"network": "mainnet"
}
-
Your add-on receives the request and creates a new instance of your add-on, based on the
quicknode-idwhich is a unique identifier for each user. Ifreferersare provided, you must forward them as headers in requests to the user's endpoint. -
You respond with a JSON object indicating success or failure, along with URLs for user access and dashboard login.
{
"status": "success", // or "error"
"dashboard-url": "http://auth.yoursite.com/access/jwt", // optional, used for SSO login
"access-url": "http://api.yoursite.com/some-token-here" // optional, used to access the service
}
Update
It is triggered when a user rotates tokens, updates referrers, or changes their plan.
- Quicknode sends a PUT
/updaterequest with payload details likequicknode-id,endpoint-id,plan, andreferers.
{
"quicknode-id": "9469f6bfc411b1c23f0f3677bcd22b890a4a755273dc2c0ad38559f7e1eb2700",
"endpoint-id": "2c03e048-5778-4944-b804-0de77df9363a",
"wss-url": "wss://long-late-firefly.quiknode.pro/2f568e4df78544629ce9af64bbe3cef9145895f5/",
"http-url": "https://long-late-firefly.quiknode.pro/2f568e4df78544629ce9af64bbe3cef9145895f5/",
"referers": ["quicknode.com"], // may be null as well if none set
"contract-addresses": [],
"chain": "ethereum",
"network": "mainnet",
"plan": "new-plan-id"
}
-
Your add-on receives the request and updates the instance of your add-on, based on the
quicknode-id. -
You respond with a JSON object indicating success or failure.
{
"status": "success" // or "error"
}
- Plan changes are pro-rated automatically by Quicknode based on the billing cycle.
Deactivate Endpoint
It is triggered when a user disables an endpoint. Since an account can have multiple endpoints, this endpoint deactivates the specific endpoint.
- Quicknode sends a DELETE
/deactivate_endpointrequest with thequicknode-idandendpoint-id.
{
"quicknode-id": "9469f6bfc411b1c23f0f3677bcd22b890a4a755273dc2c0ad38559f7e1eb2700",
"endpoint-id": "2c03e048-5778-4944-b804-0de77df9363a",
"chain": "ethereum",
"network": "mainnet"
}
- Your add-on receives the request and deactivates the specified endpoint, then responds with a JSON object indicating success or failure.
{
"status": "success" // or "error"
}
Deprovision
It is triggered when a user unsubscribes from your add-on or their payment fails (for the last time).
- Quicknode sends a DELETE
/deprovisionrequest with thequicknode-id.
{
"quicknode-id": "9469f6bfc411b1c23f0f3677bcd22b890a4a755273dc2c0ad38559f7e1eb2700",
}
- Your add-on receives the request, removes the account based on the
quicknode-id, and responds with a JSON object indicating success or failure.
{
"status": "success" // or "error"
}
Implementation Example
Quicknode provides starter code in various programming languages to help you get started quickly:
Here's an example from our Node.js starter code.
This example demonstrates the /provision endpoint from a Quicknode Marketplace add-on starter template. It handles the creation of new accounts and endpoints when a user subscribes to your add-on. The basicAuth(authInfo) middleware protects this endpoint with HTTP Basic Auth.
router.post('/provision', basicAuth(authInfo), async (request, response) => {
const [account, accountCreated] = await models.Account.findOrCreate({
where: { quicknode_id: request.body['quicknode-id'] },
defaults: {
is_test: request.headers['X-QN-TESTING'] === 'true',
plan: request.body['plan'],
},
})
console.log('Upserted account with id: ' + account.get('id'))
const [endpoint, endpointCreated] = await models.Endpoint.findOrCreate({
where: {
quicknode_id: request.body['endpoint-id'],
account_id: account.get('id'),
},
defaults: {
is_test: request.headers['X-QN-TESTING'] === 'true',
plan: request.body['plan'],
chain: request.body['chain'],
network: request.body['network'],
wss_url: request.body['wss-url'],
http_url: request.body['http-url'],
},
})
console.log('Upserted endpoint with id: ' + endpoint.get('id'))
var baseUrl = request.protocol + '://' + request.get('host')
response.json({
status: 'success',
// replace below with real URL for sso login
'dashboard-url': `${baseUrl}/dashboard`,
'access-url': `${baseUrl}/api`, // Return null if not applicable
})
})
4. No Authentication
No authentication is perfect for open services that don't require access control or user verification. This option provides the simplest integration path with minimal overhead.
Requests from Quicknode are forwarded directly to your service endpoint without any authentication headers or credentials. Your service receives the raw requests exactly as they come from users.
Implementation Example
Your service simply needs to handle incoming requests without authentication checks:
import { Router } from 'express'
const router = Router()
router.post('/rpc', async (request, response) => {
// Process the request directly - no auth needed
const { method, params } = request.body
// Your service logic here
const result = processRequest(method, params)
response.json({
jsonrpc: '2.0',
result: result,
id: request.body.id
})
})
Choosing the Right Method
Select your authentication method based on these key considerations:
Choose Custom Headers when you have:
- Existing APIs with header-based authentication
- Zero tolerance for API modifications
Choose HTTP Basic Auth when you need:
- Simple access control for private services
- Security without complexity
- Service-level authentication (not per-user)
- Quick implementation with minimal overhead
Choose Provisioning APIs when you need:
- Granular access control and user management
- Custom dashboard or user interface
- Complex business logic tied to subscriptions
Choose No Authentication when you're building:
- Open public services or APIs
- Community tools and utilities
- Services that benefit from unrestricted access
- Simple integrations requiring maximum performance
Conclusion
Quicknode's flexible authentication options make it easier than ever to integrate your services with the marketplace. Basic Auth and Header-Based Auth provide the sweet spot for most existing services, offering security and compatibility without requiring code changes. No authentication enables open services to integrate seamlessly, while traditional provisioning APIs continue to support advanced use cases requiring custom user management.
Next Step: Building Your Add-on
If you’re ready to go beyond authentication, the How to Build a Marketplace Add-On guide will walk you through the complete process of building your add-on. This guide is the best place to start building once you’ve chosen your authentication method.
We ❤️ Feedback!
Let us know if you have any feedback or requests for new topics. We'd love to hear from you.